Pathology of Acute Appendicitis – Its Etiology, Morphology, Gross Appearance & Microscopic view
Aims of the Practical
Pathological Process: Acute Inflammation
Model : Appendix
Specimen Provided : Acute Appendicitis Slide
What is Acute Appendicitis?
Histopathological Definition
Acute Appendicitis is defined as an acute inflammation of the inner lining (glandular epithelium) of the vermiform appendix that spreads to its other layers
Who gets it?
1.Mostly young people (age 10-20) but can present at any age
2.M>F : (1.4:1)
3.A common surgical disease : 7-9% lifetime risk
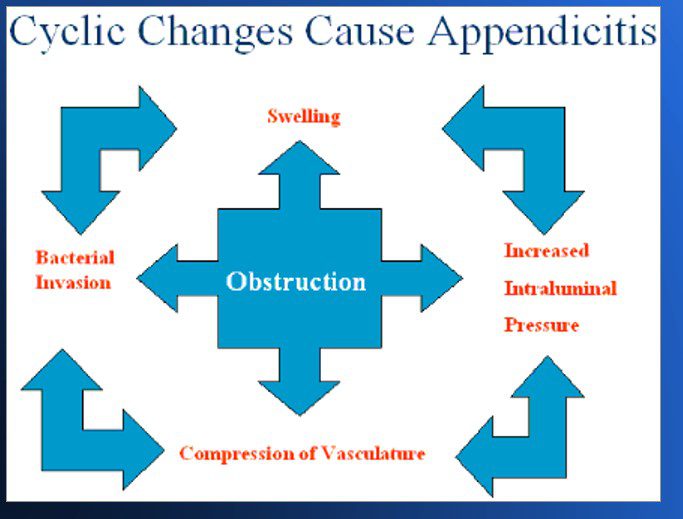
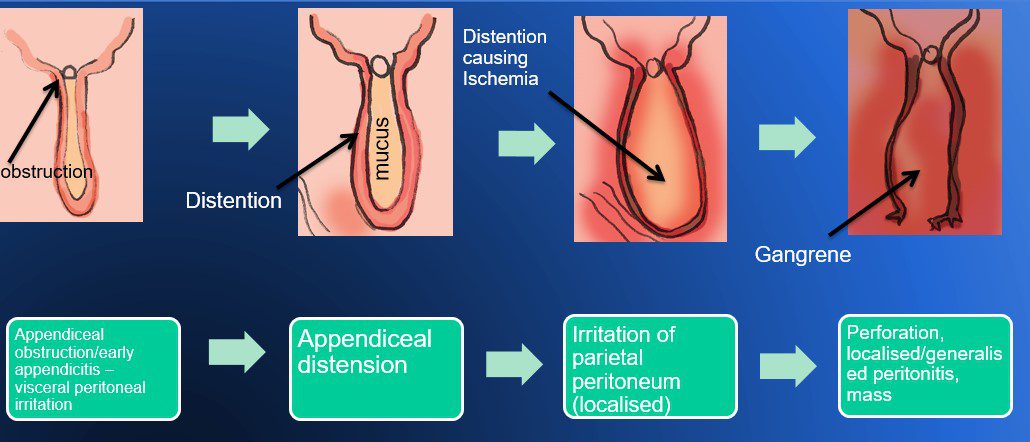
How does Acute Appendicitis Develop ?
- Obstruction of opening
- Distention
- Perforation
Cyclic Changes Causing Appendicitis
Pictorial Explanation
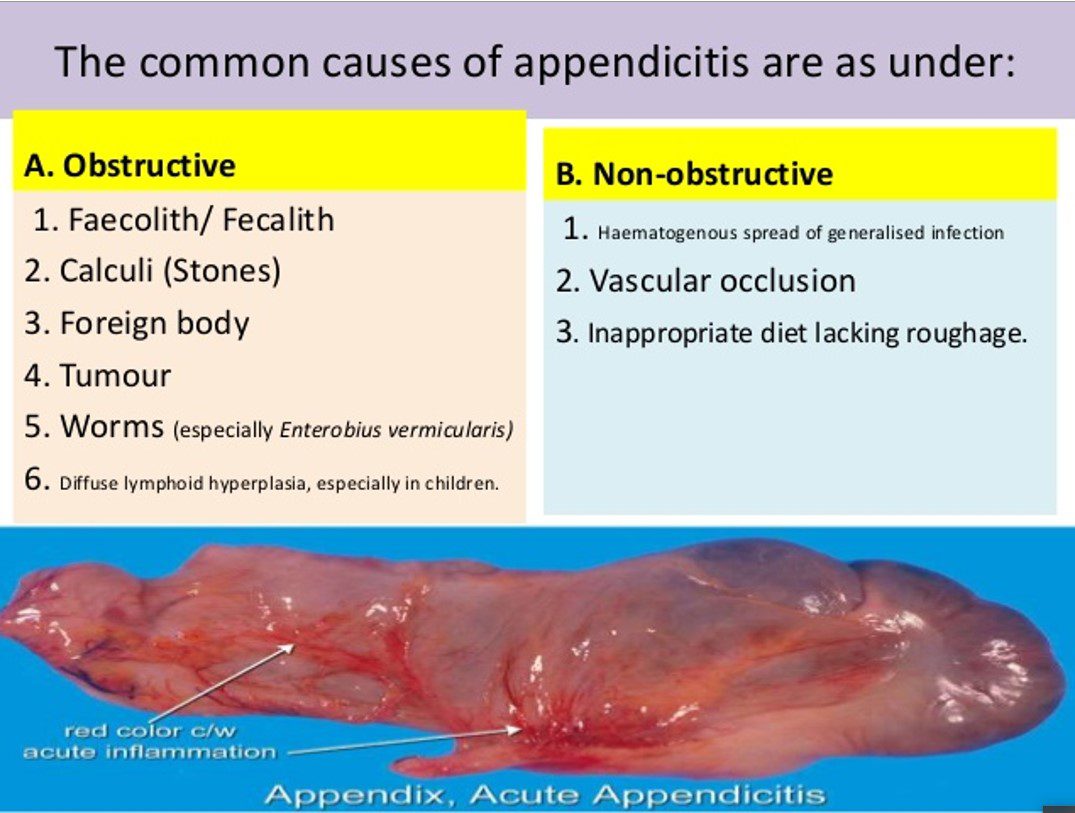
Etiology
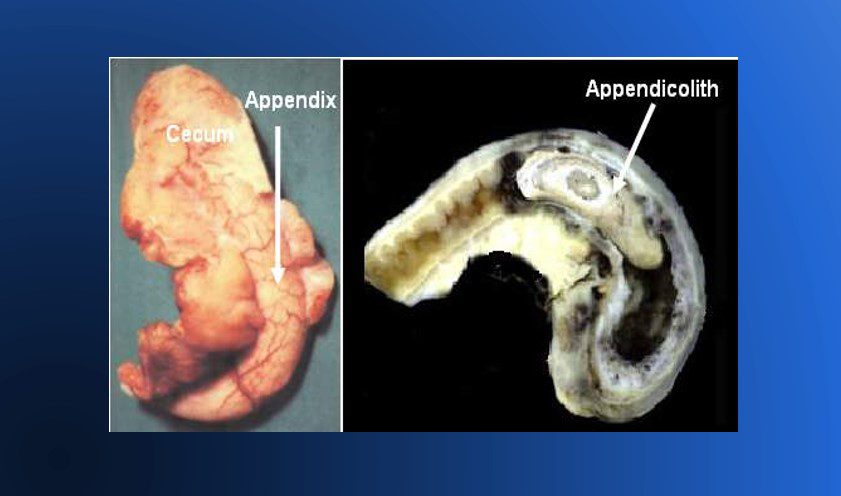
1.Fecalith
2.Gallstone
3.Ball of Intestinal Worms
4.Tumors
“Typical” Presentation
- Dull, crampy central abdominal pain
- Malaise/vomiting/anorexia/low grade fevers
- Pain worsens & localises to RIF with cough/movement tenderness
- Systemic symptoms
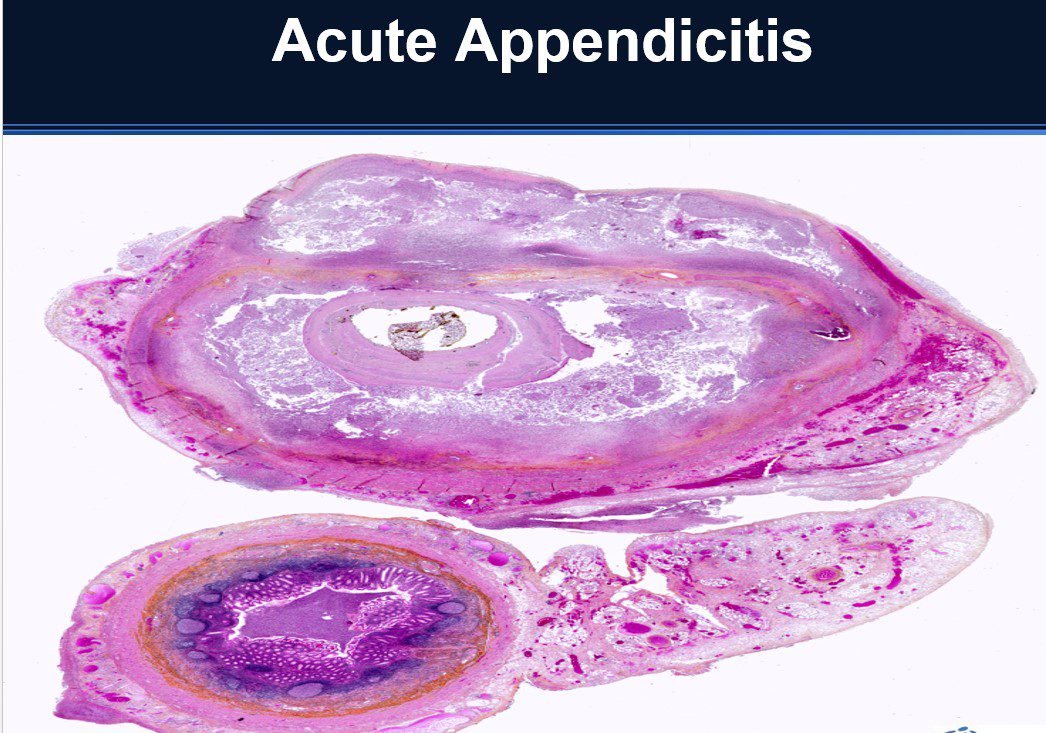
Morphology
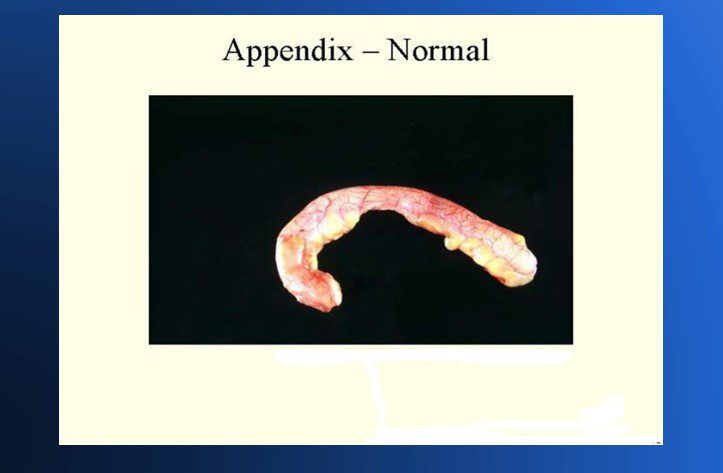
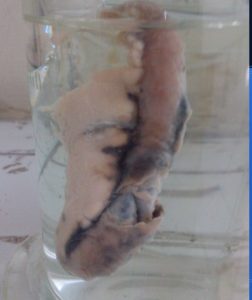
Normal Vermiform Appendix
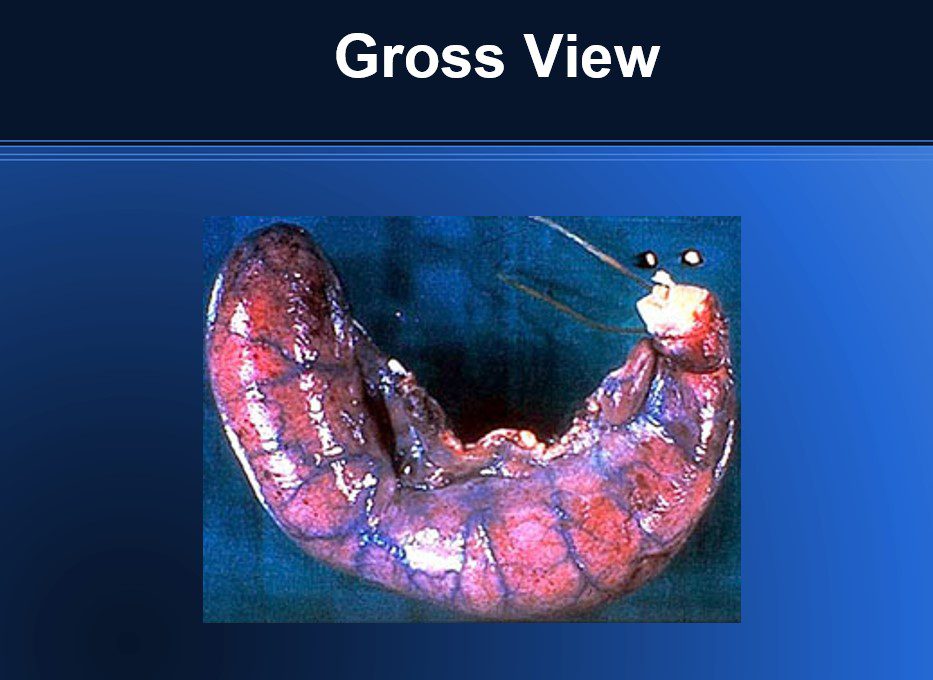
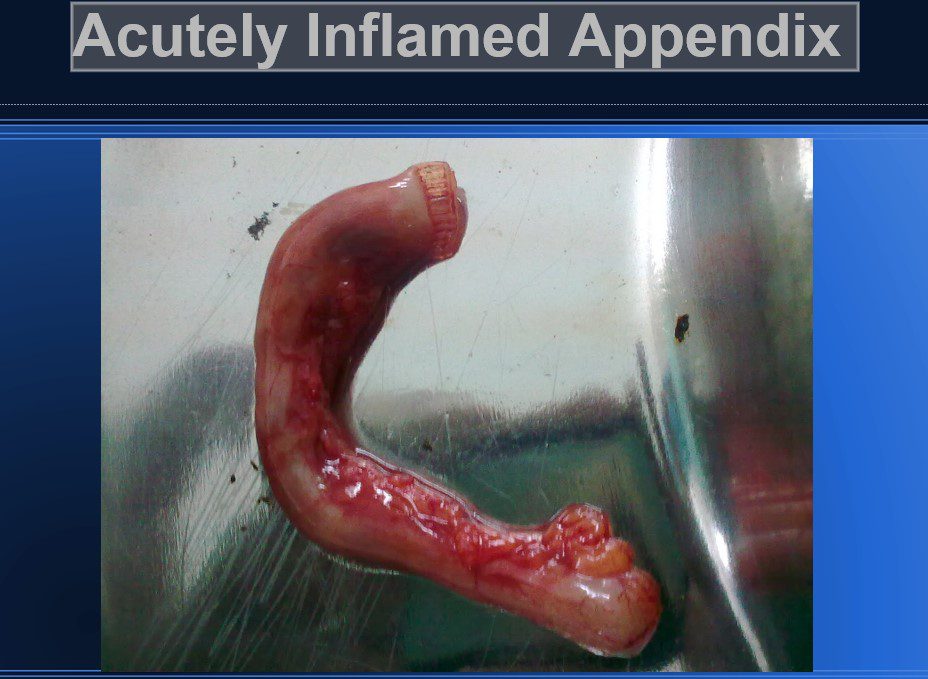
Gross Pathology
- Grossly inflamed, swollen & red.
- Prominent vessels visible on the surface
- May be covered by phlegmatic eroded tissue
Acutely Inflamed Appendix
Gangrenous Appendix ( a )
Microscopic Appearance
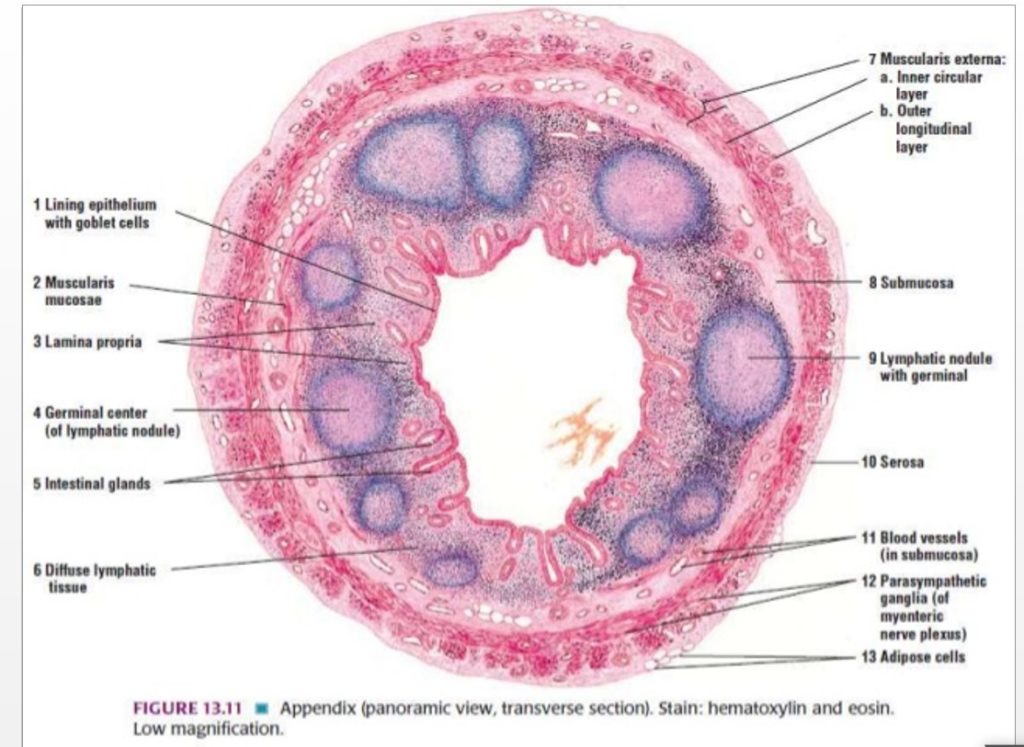
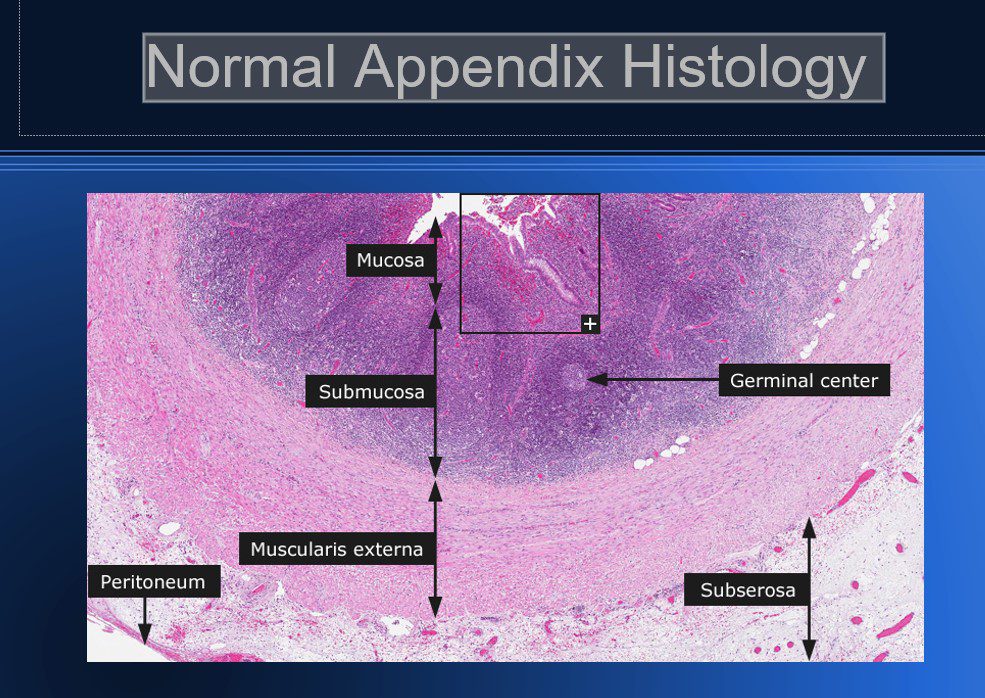
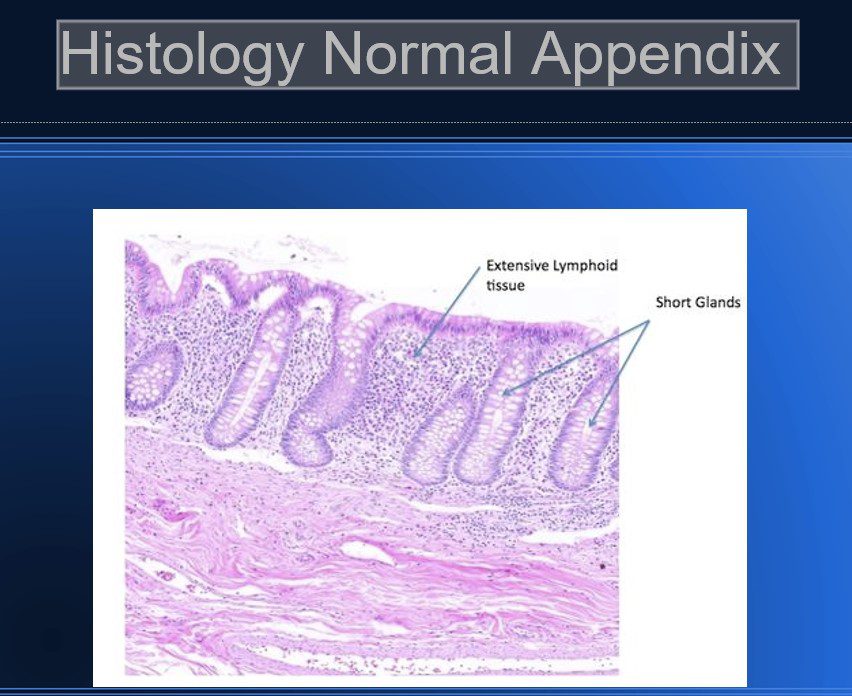
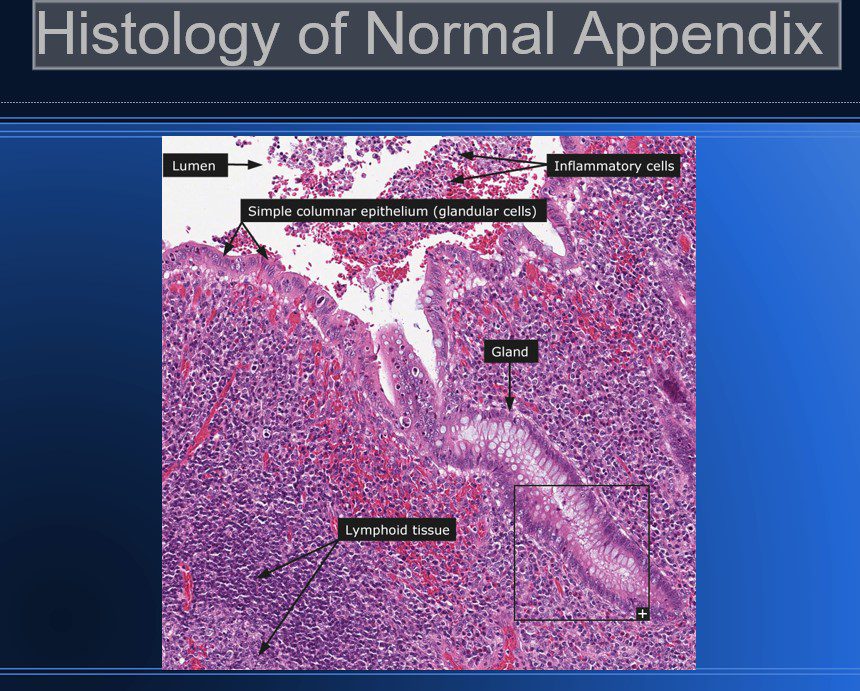
Normal Appendix Histology
- Similar histologically to the rest of the colon.
Few differences which make the appendix identifiable.
- Shorter glands (and no villi – like the colon)
- Large lymphoid nodules deep to the outer muscular wall
- Absence of the tenia coli
Histology Normal Appendix
Normal Appendix Histology
Histology Normal Appendix
Histology of Normal Appendix
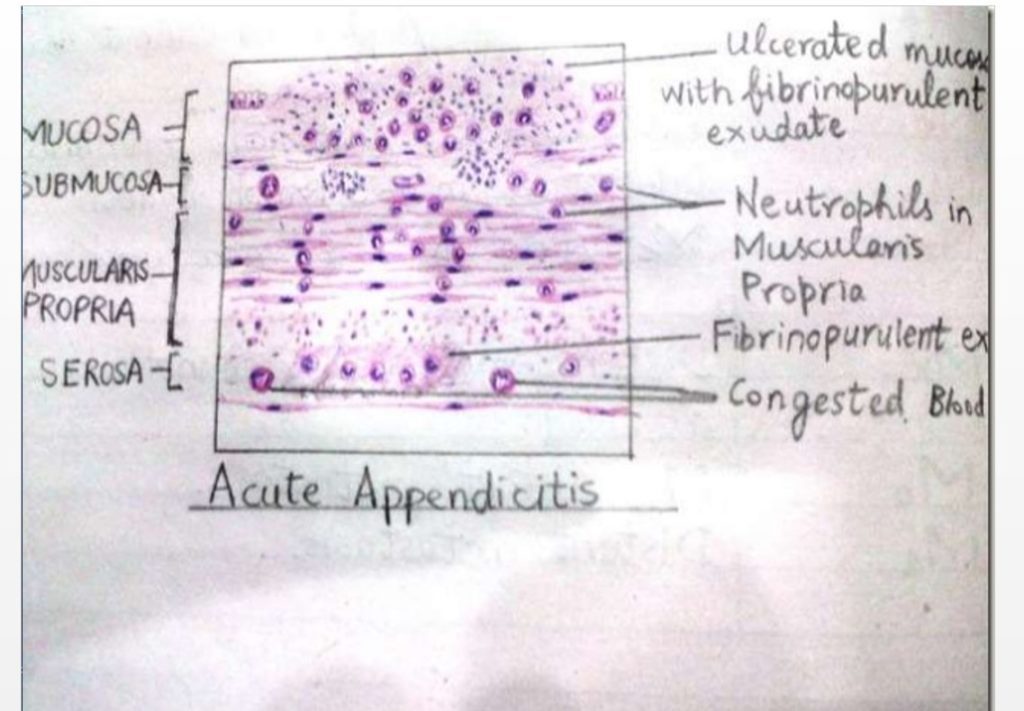
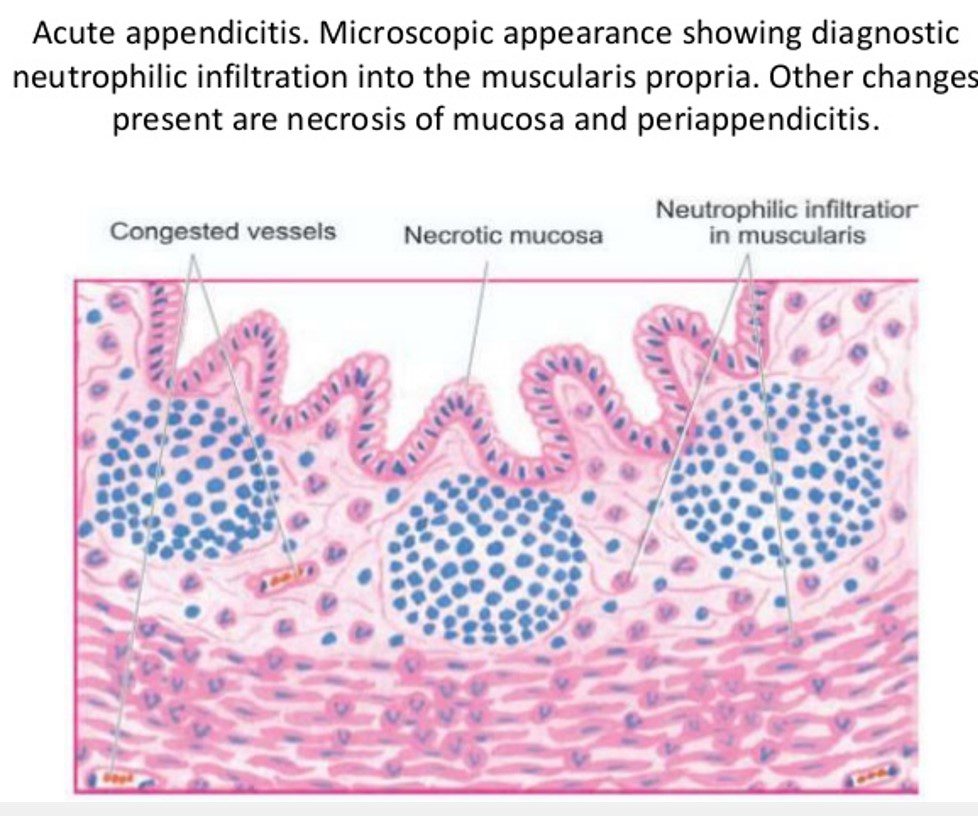
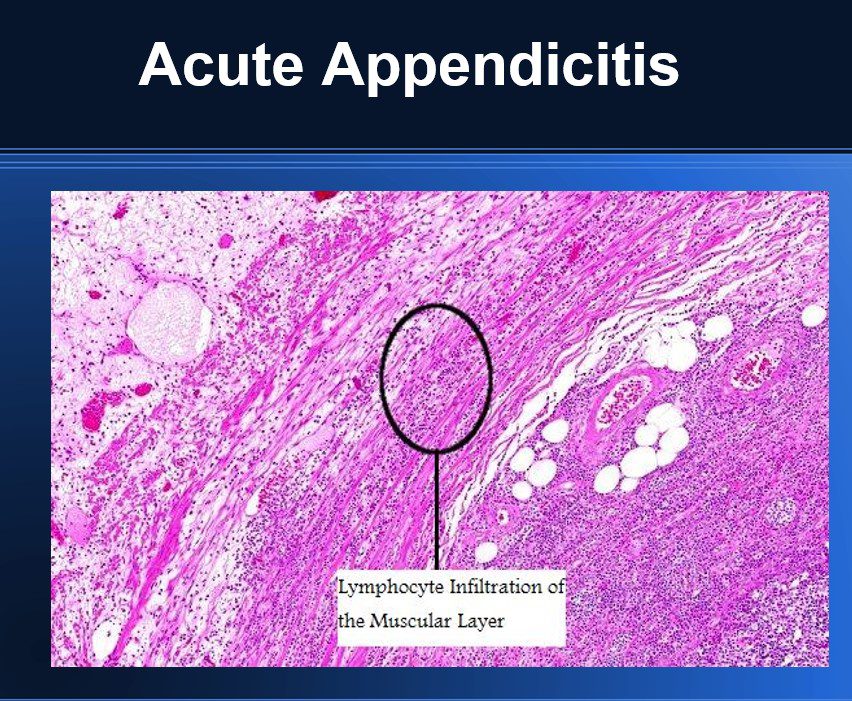
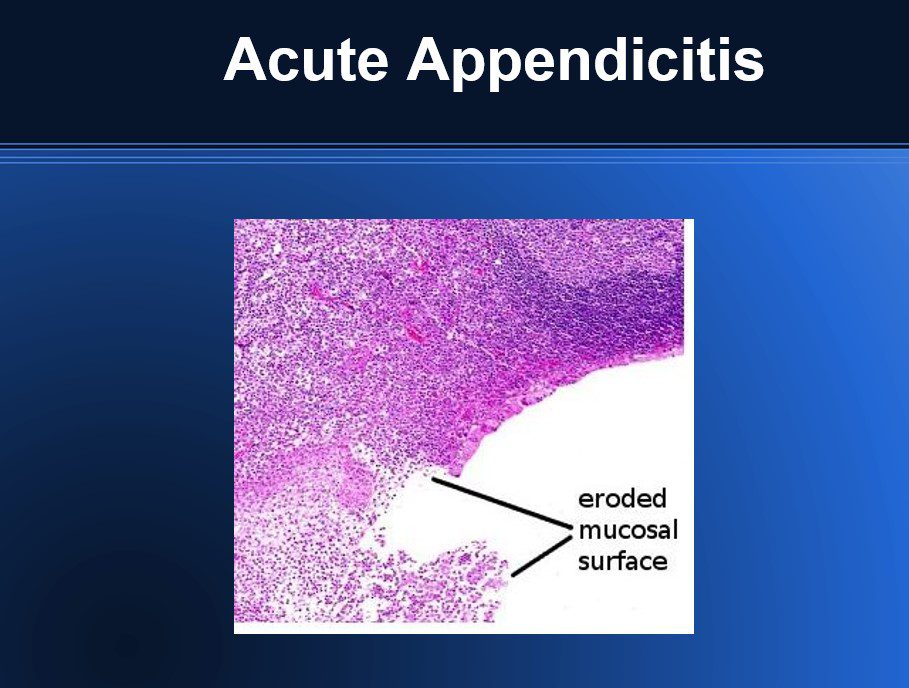
Microscopy of Acute Appendicitis
- Infiltration of PMN Cells in mucosa Infiltrating into muscularis
- Splitting of muscularis due to edema
- Edema of all layers
- Ulceration of outer layers
- Vasodilation
- Perivascular infiltration of inflammatory cells
- Intraluminal inflammatory exudates
Identification Points
- Presence of acute inflammatory cells
( Eosinophils and polymorphonuclear Neutrophils )
- Separation of muscles fibers due to edema
- Loss of mucosal lining due to bacterial overgrowth
Summary
- A common surgical emergency with high mortality if not treated well in time
- Any pain in RIF should be thoroughly investigated
- One of the commonest reason of Acute Abdomen
If you have any question regarding acute appendicitis, write it in the below comment box.








Excellent