Haemocytometer – Improved Neubauer’s chamber:
The Haemocytometer:
Haemocytometer is an apparatus used to count various blood cells (RBS, WBC, Eosinophil and platelets). It consists of RBC, and WBC pipette ( Thoma diluting pipettes) and a thick slide (Neubauer’s Chamber).
Reagents:
Hayem’s fluid for RBC counting and its composition:
- NaCl – 0.5 g for isotonicity.
- Na2SO4 – 2.5 g Break RBCs and prevents their Rouleaux formation.
- HgCl2 – 2.5 Antibacterial/antifungal and as preservative.
- Distilled H2O up to 100 ml.
Diluents for Leukocyte Counting:
Turk’s Solution is used for WBC’s counting. Its composition is as follow:
- 1.5 ml of glacial acetic acid – for a destruction of RBC’s and platelets.
- 1 ml aqueous gentian violent – to stain nuclei of WBC’s.
- 100 ml – Distal water.
Diluents for platelet counting (Rees-Ecker’s solution) and its Composition:
- 3.8 g Na citrate as anticoagulant.
- 0.2 ml neutral formaldehyde (38%) – as Antifungal and fixative for the cells.
- 0.5 g brilliant cresyl blue in 50 ml distal water – for staining of platelets.
- Distal water up to 100 ml – as diluent.
1. Haemocytometer – Improved neubauer’s chamber RBC Pipette:
I. This consist of glass stem having a capillary tube in it which opens in a bulb containing red bead and opposite to the bulb again there is a small stem. This small stem is connected to red coloured mouth piece with the help of rubber tube.
II. The stem has three markings, 0.5, 0.1 and 101. From the tip of the pipette to the marking 1.0 there are equal divisions. These are simple divisions not of any specific like mm, ml and cu mm.
III. The stem has the capacity of one part, and the bulb has 100 parts.
IV. Bead of pipette serves two purposes first mixing of blood with diluting fluid and other acts as an identification mark of RBC pipette.

2. Haemocytometer – Improved neubauer’s chamber WBC Pipette:
This pipette is similar in shape except size of the bulb is smaller, marking are 0.5, 1.0 and 11, and bulb contains white bead and colour of mouthpiece is white.

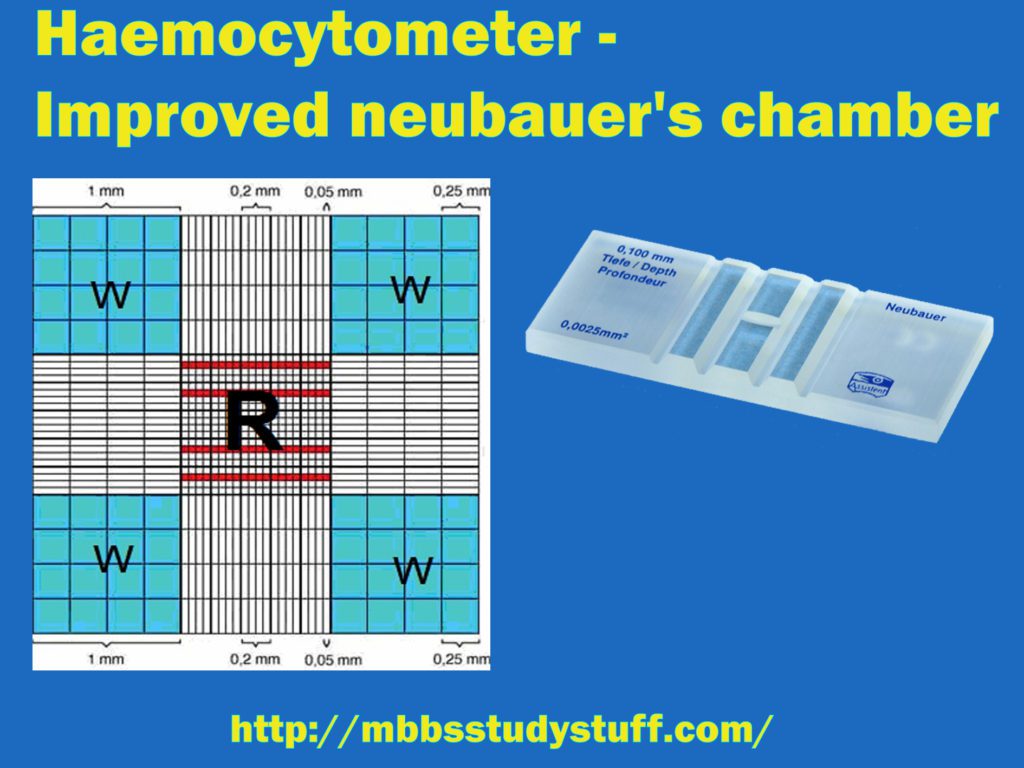
3. Neubauer’s chamber (Levy counting chamber with improved Neubauer Ruling)
- This is a thick glass having central platform divided into positions with the help of H shape groove or trench.
- On both the side of the lateral groove there are raised ridges of a height of 0.1 mm (1/10 mm) from the central platform. When a coverslip is placed on the ridges, a space of 0.1 mm height is created below the coverslip on the central platform.
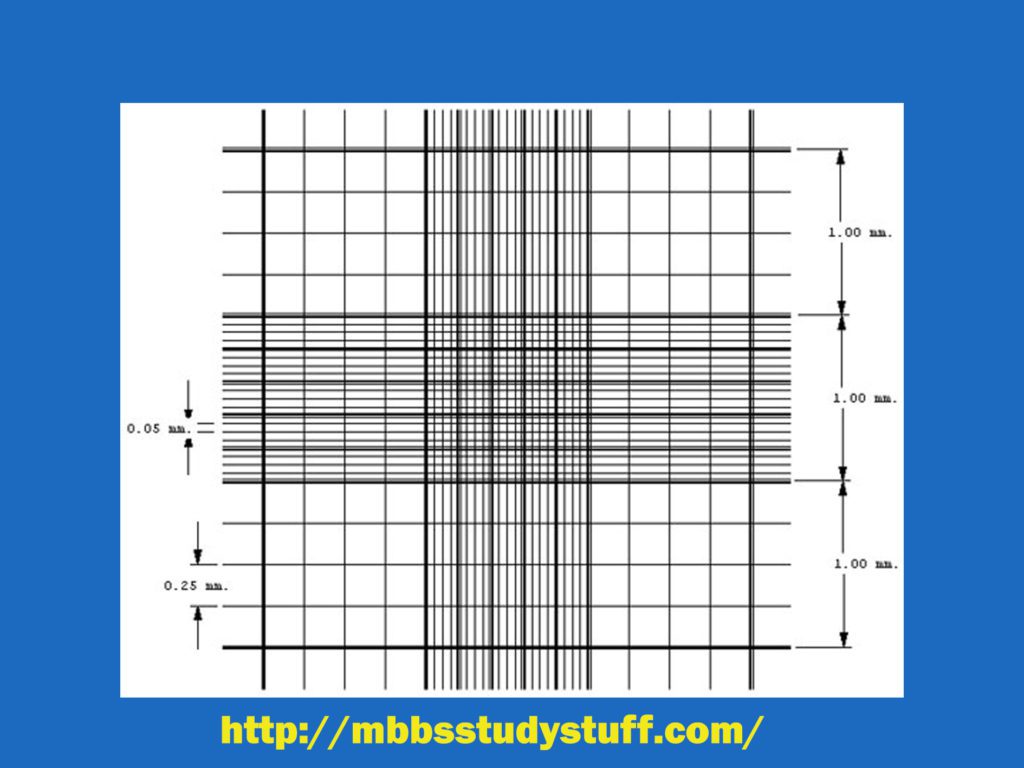
- Counting chamber (Grid) is made up of ruled area of 3mm x3 size on each central platform. Each central area is further divided by triple lines into 9 squares of equal size (1 square mm each).
- Four corner squares are further divided into 16 squares of equal size. These four corner squares are used to do total leucocytic count (TLC).
- The volume of each big square is 0.1 cu mm (1 mm x 0.1 mm).
- Central big square is divided into 25 (medium size) squares each having arm 1/5 mm. Area of each medium size square is 1/25 sq.mm (1/5 x 1/5), and the volume of each square is 1/250 cu mm (1/25 x 1/10).
- Further, these medium size square are divided into 16 small squares of equal size. Area of each small square is 1/20 mm ( 1/5 x 1/4). Area of each square is 1/400 mm² (1/20 x 1/20) and volume is 1/4000 mm³ (1/400 x 1/10). Total number of smallest squares in big central square are 400 (25 x 16).
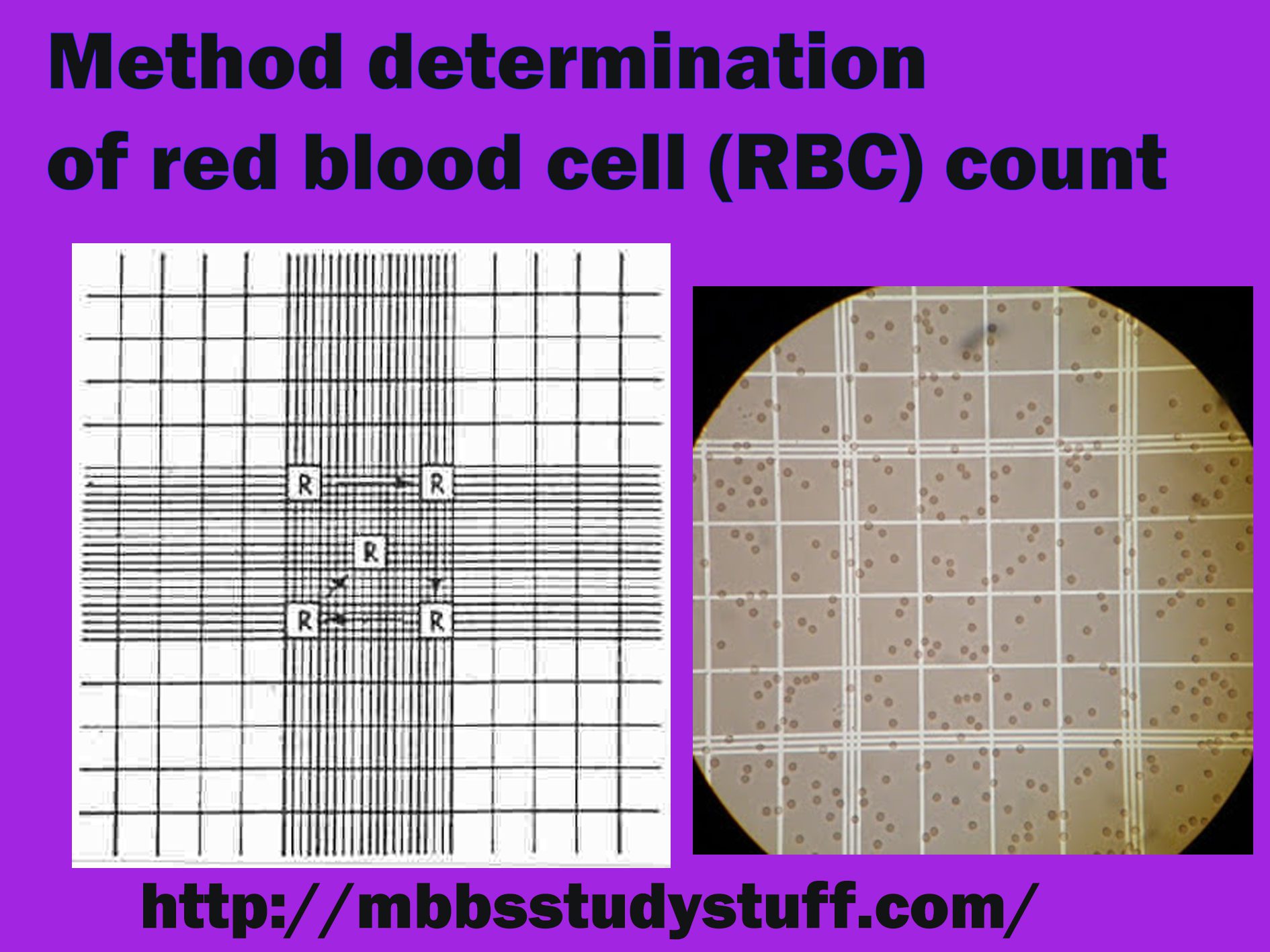
- RBCs are counted in 5 medium size square R2, R3, R4, four corners and one central.
Use of counting chamber:
RBC chamber: RBC, platelet and reticulocyte count.
WBC chamber: WBC and Eosinophils count.
Haemocytometer – Improved neubauer’s chamber Procedure:
- Clean the Neubauer’s chamber in mild detergent solution and let it dry.
- Place it on the stage of microscope and focus counting chamber in low power and study all the squares carefully.
- Turn the nose piece of microscope and focus the chamber under high power.
- Study all the chamber carefully.
Charging of chamber
It is placing of diluted blood in Neubauer’s chamber with coverslip over it. Fix the Neubauer’s chamber on the stage with clips and place coverslip over it. Now take coloured solution (Eosin in water) in the RBC pipette and touch the tip of pipette near the edge of the coverslip on the central platform at an angle of about 45 degrees and dropwise drop the fluid. The fluid enters below the coverslip because of capillary action, immediately remove the pipette.
Precautions:
- Chamber should be clean, dry and grease-free.
- There should not be overcharging (Flow of fluid in side trenches) or under charging (incomplete filling of the chamber).
- Do not hold the coverslip from its flat side (it will leave finger prints), hold it from the edges.
- If over-charging occurs, wash the chamber and recharge.
B. COLLECTION OF BLOOD SAMPLE IN Haemocytometer – Improved neubauer’s chamber
Blood is collected for various haematological investigations.
CAPILLARY BLOOD
i. It can be collected from fingertip and ear lobule in adult and heal in case of newborn or infant.
ii. Take 20-24 gauge sterilized disposable hypodermic needle for this purpose.
iii. Clean ring finger of left hand (preferably ring finger) with spirit swab and let it dry. Sterilization is effective when spirit dries up and spirit causes haemolysis when it comes in contact with blood.
iv. Give 2-3 mm deep prick at centre of the tip of ring fingers so that free flow of blood will be there.
v. After collection of blood sample put a spirit swab at pricking site and hold it there for 23 minutes (till bleeding stops) Vi. Do not squeeze the finger for
vi. Do not squeeze the finger for collection of blood, it will cause dilution of blood because tissue fluid mixes with blood.
VENOUS BLOOD
i. Take 5 ml disposable syringe with 19-20 gauge needle.
ii. Support the arm of the subject on the edge of the table and locate the vein in antecubital fossa (area).
iii. Clean the area with spirits swab and let it dry. Do not touch the area again with finger once it is cleaned.
iv. Apply rubber or cloth tourniquet around the arm to occlude venous return. Ask the subject to close and open the fist repeatedly so as vein gets engorged with blood.
v. Place the thumb of your left hand on the skin about 4-5 cm distal to the vein to be pricked so that vein will not slip.
vi. Introduce the needle into the skin and push the needle on the side of vein, when needle enters the vein resistance feels to cease.
vii. Draw the blood in syringe slowly to the required quantity (slowly means not faster than the filling of vein).
viii. Release the tourniquet and withdraw the needle after putting the fresh Spirit swab at the site of the puncture of skin.
ix. Ask the subject to press the swab at the site of the puncture of skin.
x. Eject the blood from the syringe after removing needle in the vial having anticoagulant. For serum no anticoagulant is required in the vial.
Anticoagulants Used in Haemocytometer – Improved neubauer’s chamber
1. Ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA):
- Calcium chelating agent
- No effect on blood cells
- 2.4 mg dry powder in a vial for 2 ml of blood (1.2mg/ml of blood)
- Used for ESR and PCV measurement.
2. Sodium citrate:
- Calcium chelating agent
- 0.4 ml of 3.8% solution for 1.6 ml of blood
- used for ESR and collection of blood from donors 3. Double oxalate mixture:
3. Double oxalate mixture:
- Potassium oxalate and ammonium oxalate in the ratio of 2:3.
- Single oxalate is not used mainly to measure PCV.
- Because potassium oxalate causes shrink-age of cells and ammonium oxalate causes increase in volume of the cells.
4. Heparin:
- Solution or powder may be used according to need.
- Does not affect cell volume
Haemocytometer – Improved neubauer’s chamber PRECAUTIONS
1. Must not interchange the pricking needle.
2. Preferably use a needle for pricking once.
3. . If necessary to reuse the needle in the same subject, sterilize it on spirit lamp (a spirit does not kill hepatitis virus).
4. Do not use single oxalate anticoagulant for measuring PCV.
5. Destroy the needle before disposing it off.



What is the procedure of neubauer’s chamber