How to measure heart rate from ECG:
Before going to calculate heart rate from an ecg strip. Lets me give a short introduction to ECG and its leads.
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
Graphic recording of electrical potential generated due to transmission of depolarization wave (or cardiac impulse) through the heart, and due to its spread into surrounding tissue and body surface. Is called electrocardiogram (ECG).
Father of ECG
Einthoven (1903)
Significance
(1) Site of pace-maker is recorded
(2) Heart. Rate can be calculated
(3) Rhythm of heart can be recognised
(4) The voltage produced due to potential changes in the heart can be calculated.
(5) Helps to diagnose heart diseases.
Waves of ECG
(I) P Wave: produced by atrial depolarization.
(2) QRS Complex: Produce by ventricular depolarization.
(3) ST Segment and T Wave: Produce by ventricular repolarization (Ganong)
(4) Atrial T Wave: It is a depression in PR segment, usually obscured by QRS complex. Produced by atrial repolarization; Seen in (a) Sinus tachycardia (b) Hypertrophied atria.
(5) U Wave
(Inconstant). Produced by slow repolarization of the papillary muscle. Seen in hypokalemia
PQ or PR Interval
It shows
(1) Time interval b/w onset of atrial contraction and onset of ventricular contraction. OR
(2) AV nodal delay
Value
- 16 second (120-210 msecond)
QT Interval
It shows a duration of ventricular contraction (from the
beginning of Q (or R) wave to the end of T wave).
Value
0.35 second
Total Time Period Of ECG
it shows time for one heart beat.
Value
0.83 second
Calculation of Heart Rate From it
In 1 sec. Heart beats-1 time
In 60 sec. Heart beats-1/0.83 time
So, Heart Rate = 72 beats / min
Calculation of Heart Rate From ECG
(1) Calculate smallest squares b/w 2 successive R waves and divide it by 1500. The result is Heart Rate.
(2) Calculate large squares b/w 2 successive R waves and divide it by 300, Result is Heart Rate.
(3) If the cardiac rhythm is irregular, then count QRS complexes in 15 large squares, multiply it by 20, Result is Heart Rate.
Recording of ECG
Apparatus
Electrocardiograph
Kinds
Two
(1) Pen recorder(old)
(2) Oscilloscope(modern)
Electrical Current In Partly Depolarized Heart
(1) Base is negative
(2) Apex is positive
Electrocardiographic (ECG) Leads
Conventional electrode system that carries electrical potential from body surface to electrocardiograph while recording ECG, are called electrocardiographic
leads
Types
(1) Bipolar limb leads
(2) Precordial (chest) leads
(3) Augmented unipolar limb leads.
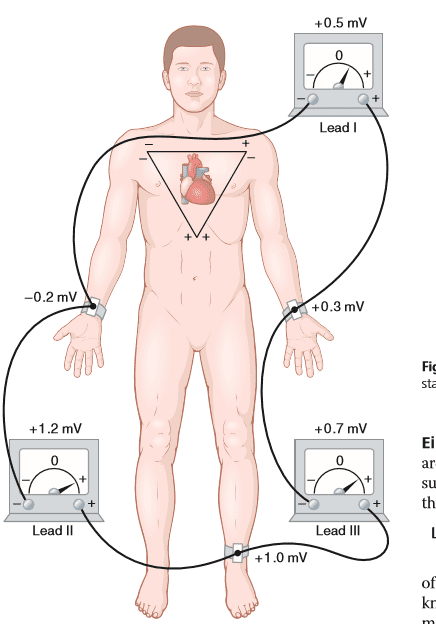
Bipolar Limb Leads
Here ECG is recorded from two specific electrodes connected to limbs.
Types
Three
(1) Lead l
+ ve terminal j Left arm
-ve terminal + Right arm
(2) Lead II
-ve terminal + Right arm
+ ve terminal + Left leg
(3) Lead III
+ ve terminal + Left leg
-ve terminal + Left arm
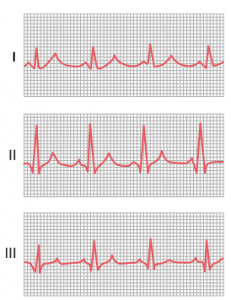
lead I , lead II and lead III
Precordial (Chest) Leads
Here ECG is recorded by placing + ve electrode to one of six separate positions on chest over heart and by connecting -ve (or indifferent) electrode simultaneously to right arm, left arm and left leg,
Six Precordial Positions
V1 = 4th intercostal space 1 inch away from right
sternal border
V2 = 4th intercostal space 1 inch away from left
sternal border
V3 = Mid-point b/w V2 and V4
V4 = 5th intercostal space at left mid-clavicular
line
V5 = Point where anterior axillary line cuts
perpendicularly the horizontal line extended
from V4
V6 = Point where mid-axillary line cuts
perpendicularly the same horizontal litre
extended from V4
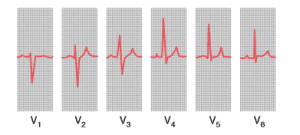
V1, v2, v3, v3, v4, v5 and v6
Note
(1) QRS complex of V1 and V2 is -ve because they are towards base of heart (-ve)
(2) QRS complex of V4, V5 and V6 is + ve; because they are towards apex of heart(+ ve)
Augmented Unipolar Limb Leads
Here two limbs are connected to -ve terminal while the third limb to + ve terminal; this positive terminal is known as follows:
(1) aVR Lead: When + ve terminal is connected to right arm
(2) AVL Lead: When + ve terminal is connected to left arm
(3) aVF Lead: when + ve terminal is connected to left leg
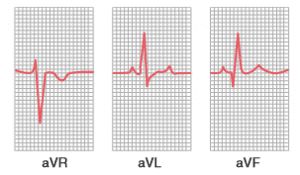
AvR, AVL and avF






Leave a Reply