Heart Block:
Block of impulse transmission at any critical point from pace-maker SA node through conductive pathway of heart, is called heart block
Types
(1) Sino-atrial block
(2) Atrio-ventricular block
(3) Right or left bundle branch block
(4) Arborization block
Sino-Atrial Block
When impulses from SA node is blocked before it enters atrial muscle, it is called sino-atrial block.
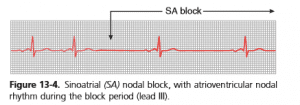
Sino-atrial block
Characteristics
(1) Sudden cessation of P wave in ECG
(2) Atria does not contract, resulting in missing of 1 complete heart beat
(3) After sometimes AV node becomes pace-maker and ventricle contracts with a new rhythm; so, QRS complex is not completely absent in ECG.
Atrio-Ventricular Block
When impulse from atria (SA node) cannot enter ventricles due to block at AV node or AV bundle (bundle of His), it is called atrioventricular block.
causes
(1) ischemia of AV nodal fibres due to coronary insufficiency
(2) Compression of AV bundle by scar tissue or calcified plaque or atherosclerotic plaque.
(3) Inflammation of AV node or AV bundle due to myocarditis as in diphtheria and rheumatic fever.
(4) Para-sympathetic (vagal) over-stimulation of heart as in carotid sinus syndrome
Types of Atrio-Ventricular Block
Three types:
(I) First Degree Incomplete Block
In this, all impulses from atria are transmitted very slowly to ventricles, causing prolonged PR interval> 220 msec (0.20 sec). (Normal PR interval is 120-210 msec i.e., 0.16 sec).
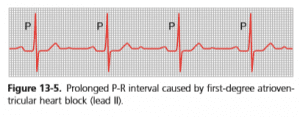
First degree Heart block
(II) Second Degree Incomplete Block
ln this impulse passes into ventricles after one atrial contraction and fails to pass after next, Second-degree alternating b/W conduction arid non-conduction and causing dropped contraction of ventricles.
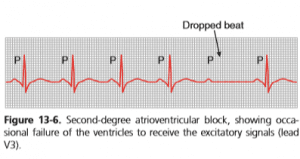
Second-degree heart block
Mobitz I (Werckebach): PR interval progressively lengthens.
Mobitz II: no measurable lengthening of the PR interval.
(III) Third Degree Complete Block
In this, impulses from atria cannot pass into ventricles, so that atria contract at rhythm of SA node and ventricle contract at their own natural rhythm (which is slow), Atria & ventricles beat independently. The ECG is characterized as having no correlation between P waves and QRS complexes. Because of differences in the intrinsic rates of pacemaker tissue, the frequency of P waves is greater than the frequency of QRS complexes.
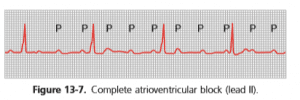
Complete heart block
Right or Left Bundle Branch Block
In this, impulse transmission through, right or left bundle branch of Purkinje fibers is blocked.
Features
(1) Ventricles of normal side will contract little earlier than blocked one, producing duplication of first heart sound.
(2) QRS complex 15 prolonged
Arborization Block
In this, impulse transmission through Purkinje fibers is blocked.
Found in:
Chronic myocardial damage






Leave a Reply