Fehling’s test:
Fehling’s test is a specific test for reducing sugar.
PRINCIPLE:
The principle of fehling test is same to that of benedict’s test. In the presence of reducing sugar, cuso4 gives cupric ion in an alkaline medium which reduces to cuprous ion.
REAGENTS:
Fehling’s A reagent: Solution A Copper sulfate solution (Cuso4)
Fehling’s B reagent: Sodium-potassium titrates and potassium hydroxide.
These solutions are preserved in separate bottles. Fehling’s reagent forms by mixing equal volumes of solution-A with solution-B.
2. Original solution (O.S) containing a carbohydrate.
PROCEDURE:
- Take 1ml of each fehling A and B solution in the same test tube.
- Add 2ml of distilled water and boil it.
- When no precipitate is formed, then add 0.5ml of original solution is in the test tube and boil it again.
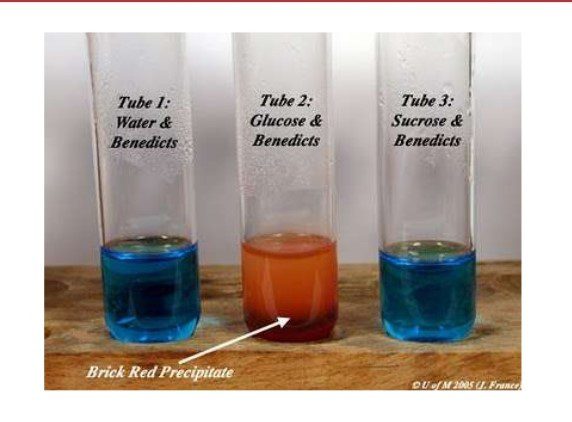
INDICATION:
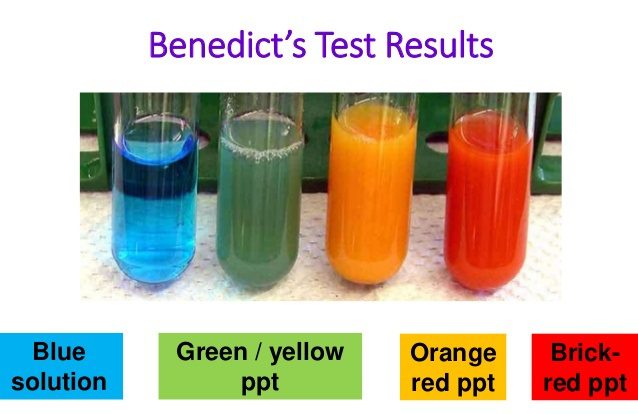
The production of yellow or brownish-red precipitate of cuprous oxide indicates the presence of reducing sugars in the sample.
RESULT:
Reducing sugar is present.
Precautions:
- Wash the apparatus before and after the experiment.
- Mix and boil the sample carefully.







Leave a Reply