Einthoven’s Triangle
Einthoven’s Triangle is an equilateral triangle drawn arbitrarily around an area of the heart, apices of which is represented by the right arm, left arm and left leg.
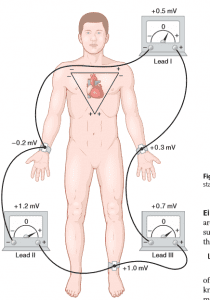
Einthoven’s triangle
Einthoven’s Law
Statement
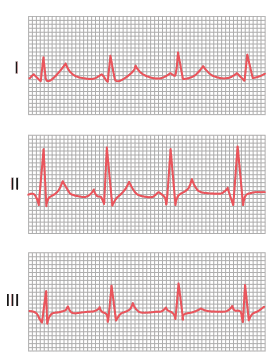
If the electrical potentials of any two of the three bipolar limb leads are known at any given instant, the third one can be determined by summing the two.
e.g ; II=1 + III
Normal P Wave
Indicates
(1) Impulse is originating at SA node It spreads over atria
(3) There is no defect of conduction
(4) Strength of contraction, mass of atrial musculature, and its nutrition are normal
(5) Impulse arrives at AV node at the summit of P wave. Abnormalities of P Wave
(1) Inverted P Wave: Caused by shift of pace-maker from SA node to AV node
(2) Absent P Wave: · Caused by atrial fibrillation
(3) P-mitral Large and notched P Wave: Caused by left atrial hypertrophy
(4) P-pulmonale Tall and peaked P Wave: Caused by right atrial hypertrophy
(5) In nodal rhythm direction of P W is reversed. Abnormalities of QRS Complex
(1) High voltage of QRS complex: Caused by right ventricular hypertrophy (in stenotic pulmonary vaIve ) and Left ventricular hypertrophy (In hypertension)
(2) Decrease Voltage of QRS complex is caused by old myocardial infarction, fluid in pericardium, etc.
(3) Prolonged QRS complex: caused by Hypertrophy of or dilation of left or right ventricle and block of Purkinje system
(4) Bizarre or odd QRS complex: caused by destruction of cardiac muscles in various areas and its replacement by scar tissue and block in conduction of impulse in Purkinje system
Current of Injury
Current flow from pathologically depolarised (injured area = -ve ) area to normally polarised (uninjured area = +ve ) is called current of injury.
Causing Factor
(1) Mechanical trauma
(2) Infectious process
(3) ischemia of local areas of heart muscle caused by Coronary occlusion, acute anterior wall infarction.
Effect on ECG
Current of injury causes an initial record (below in I and above in II and III) before QJZS complex,
J POINT
Point at which potential of ECG is exactly zero, is called J point,
Location
At the very end of QRS complex when depolarization wave completes its passage through the heart and no current flows through the heart.
Use
J point uses to plot axis of current of injury, thereby locating injured area of heart,
ST Segment Shift
when ST segment and TP segment of ECG arc not at the same potential level, it is called ST segment shift.
Occurs
When current of injury is present.
Abnormalities of T-Wave
(1) Opposite polarity of T wave to that of QRS complex Caused by delayed impulse
transmission through ventricles, eg: bundle branch block
(2) Inverted (-ve) T wave: Caused by ischemia of apex of ventricles
(3) Biphasic (one-half positive and another half negative) T wave caused by digitalis toxicity (used in coronary insufficiency to increase strength of cardiac muscle contraction)
ECG Findings of Myocardial Infarction
(1) T wave inversion
(2) ST segment elevation
(3) Deep Q wave
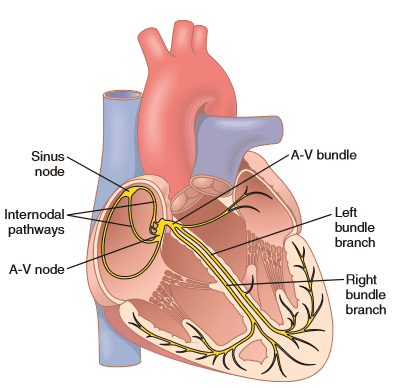
His Bundle Electrogram (HBE)
It is a record of electrical activity of heart obtained with a catheter containing ring electrodes at its tip that is passed through a vein to right side close to the tricuspid valve.
Parts of HBE
(1) A deflection
(2) H spike
(3) V deflection






Leave a Reply